|
Brain is most complex part of human body and its processes are still more complex. Modern scientists and psychologists are experimenting on it for so many centuries but are not able to conclude its functioning. Ancient Hindu Rishis elaborated its functioning and intricacies which are discussed in this article.
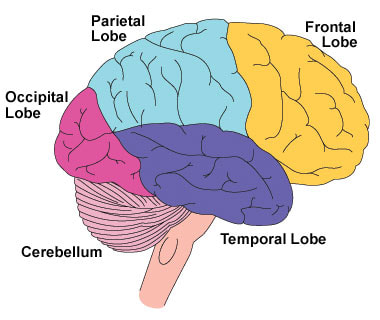
Brain commands, controls and coordinates the activities of the body. It is the “Decision making Centre”. According to modern science, Hardware of Brain include 86 billion of neurons (i.e. electrically excitable cells) and non-neuronal cells (i.e. glial cells which maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide structural & metabolic support to neurons). Anatomically, the brain is composed of the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem and Diencephalon. Various parts of brain govern intelligence, creativity, emotion, regulation of body functions, sensory & motor functions decision making. Symbolically, cognition, thought, intelligence, etc. represent software of brain. Modern Science has stuck up mostly on hardware of the brain and its functions. In contrast, ancient scientists of Hinduism deeply probed on the process of Antahkarna (the internal instrument). As per Kapil’s Samkhya Darshan, Intellect & Intelligence (Buddhi or Mahat, the place of decision-making), Ego (the self-consciousness or Ahamkara or pride or asmita) and Mind (Manas, the place of thought) form the group called the Antahkarana. The first evolution of prakriti or material is buddhi (intellect & intelligence or Mahat). Mahat in turn produces ahamkara, the ego i.e.”I” or “mine”. From ego, manas is produced. Katho Upanishad has compared the human body and Chariot i.e. Chariot as human body, master of chariot as soul (jivatma), charioteer as buddhi, reins as mind & horses as senses. According to Patanjali muni, Chitta is the the seat of soul's entanglement with Prakriti or nature. Chitta is identified as intellect, ego, mind and five sense organs. Karmic account accumulated in present & past lives, is root cause of pleasures and miseries which are evident in current birth or future. It reminds us, the Snake and Ladder game. If the counter lands at the bottom of a ladder, you can move up to the top of the ladder. If the counter lands on the head of a snake, you must slide down to the bottom of the snake. The lesson of this Indian ancient game is that it represents a life journey complicated by virtues (ladders) and vices (snakes). One who keeps trying and does not enter into negative cycle may be successful in the end. The person is provided ample opportunity to erase the each impression which create impulses in form of desires. These impulses can be amended at thought-level, decision-making level and ego-level. It is discussed in detail latter. Bhagwan Krishna laid importance of resolve (Sankalp) in Bhagwat Gita. The various aspects of brain are discussed hereunder: Anatomy of Brain: As per modern science, brain has mainly four parts as under:
Generation of thoughts is one of the major processes of mind. Experts estimate that the mind thinks between 60,000 – 80,000 thoughts a day. These thoughts are either positive or negative. As per modern science, the thoughts are mostly negative and triggered by external stimuli. There is an old saying, “Watch your thoughts; for they become words. Watch your words; for they become actions. Watch your actions; for they become habits. Watch your habits; for they become character. Watch your character for it will become your destiny. ” Negative thoughts prevent from focusing on the subject, drain the energy of the body and prevent from enjoying pleasant moments. Recurrent negative thoughts take the person into negative cycle which has far-reaching consequences. It creates depression and anxiety. As per Hinduism, thought materializes and becomes an action. Good thoughts lead to virtuous actions. The negative thoughts can be controlled by the following means:
As per Samkhya Darshan of Kapil muni, child is born with certain tendencies caused by actions done in past life which may not be necessarily inherited. Generally, physical configurations are inherited. These tendencies are of three types (sattva being goodness, compassion, illumination, and positivity; rajas being activity, chaos, passion, and impulsivity, potentially good or bad; and tamas being the quality of darkness, ignorance, destruction, lethargy, negativity) which create constant impulses in mind to trigger actions which may be negative or positive. Intellect & intelligence In modern psychology and neuroscience, a distinction is made between intellect and intelligence. Intellect is the ability to identify and analyse, memorize, and categorize, the physical characteristics and implications of whatever thing or event is perceived by the senses. Intelligence determines the course of action to be taken. In Samkhya philosophy, Mind is receptive and discriminating faculty which receives and individualise the impressions made by the outward objects on the senses. These are submitted to ego and by which an attribute of personality is given, thereafter it passes through intellect. Intellect present is it in distinct form. The Jivatma (soul), as an audience, beholds these presentations, as objects are seen in the mirror. In presence of Jivatma, the three dimensional energies or gunas (Sattva, Rajas and Tamas) of nature or Prakriti (including intellect, mind and ego) come alive. Awareness about oneself permits a person to know what they need to work on. Hence, self-awareness provides an opportunity to ameliorate the decisions taken in rush of temper or due to impulse created by negative thoughts. Ego As per Encyclopaedia Britannica, Ego is that portion of the human personality which is experienced as the “self” or “I”. According to Freud's personality theory, 1923, the psyche is structured into three parts, the id, ego and superego, all developing at different stages in our lives. The id is the primitive and instinctual part of the mind that contains sexual and aggressive drives and hidden memories, the super-ego operates as a moral conscience, and the ego is the realistic part that mediates between the desires of the id and the super-ego. According to Samkhya Darshan, Ahmkara comes into being as proximity of two realms – consciousness or jivatma and unconsciousness or prakriti. Ego or Ahmkara provides basis for subject –object relationship. Ahmkara stands for the bifurcation of consciousness or true self and empirical “I” which is the root cause of ignorance and miseries. Sant Kabir has explained the above in his doha as under: जब मैं था तब हरि नहीं अब हरि है मैं नाहीं । प्रेम गली अति सांकरी जामें दो न समाहीं ॥ अर्थ: जब तक मन में अहंकार था तब तक ईश्वर का साक्षात्कार न हुआ. जब अहम समाप्त हुआ तभी प्रभु मिले. जब ईश्वर का साक्षात्कार हुआ – तब अहम स्वत: नष्ट हो गया. ईश्वर की सत्ता का बोध तभी हुआ जब अहंकार गया. प्रेम में द्वैत भाव नहीं हो सकता – प्रेम की संकरी – पतली गली में एक ही समा सकता है – अहम् या परम ! परम की प्राप्ति के लिए अहम् का विसर्जन आवश्यक है. Sankalp (Resolve, संकल्प) & Success In Sanskrit language, Sankalp means determination, oath, resolve etc. Bhagwan Shree Krishna has laid importance of determination verse 24 of chapter 6. (संकल्पप्रभवान्कामांस्त्यक्त्वा सर्वानशेषतः। मनसैवेन्द्रियग्रामं विनियम्य समन्ततः॥) Patanjali’s Yoga Sutra prescribes as under:
Swami Vivekananda emphasized as under: "Take up one idea. Make that one idea your life – think of it, dream of it, live on that idea. Let the brain, muscles, nerves, every part of your body, be full of that idea, and just leave every other idea alone. This is the way to success."
0 Comments
|
Archives
March 2024
Categories
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed